Keypad Library
The mikroPascal PRO for 8051 provides a library for working with 4x4 keypad. The library routines can also be used with 4x1, 4x2, or 4x3 keypad. For connections explanation see schematic at the bottom of this page.
Note: Since sampling lines for 8051 MCUs are activated by logical zero Keypad Library can not be used with hardwares that have protective diodes connected with anode to MCU side, such as mikroElektronika's Keypad extra board HW.Rev v1.20
External dependencies of Keypad Library
| The following variable must be defined in all projects using Keypad Library: | Description: | Example : |
|---|---|---|
var keypadPort: byte; sfr; external; |
Keypad Port. | var keypadPort: byte at P0; |
Library Routines
Keypad_Init
| Prototype |
procedure Keypad_Init(); |
|---|---|
| Returns |
Nothing. |
| Description |
Initializes port for working with keypad. |
| Requires |
|
| Example |
// Initialize P0 for communication with keypad var keypadPort : byte at P0; ... Keypad_Init(); |
Keypad_Key_Press
| Prototype |
function Keypad_Key_Press(): byte; |
|---|---|
| Returns |
The code of a pressed key (1..16). If no key is pressed, returns 0. |
| Description |
Reads the key from keypad when key gets pressed. |
| Requires |
Port needs to be initialized for working with the Keypad library, see Keypad_Init. |
| Example |
var kp : byte; ... kp := Keypad_Key_Press(); |
Keypad_Key_Click
| Prototype |
function Keypad_Key_Click(): byte; |
|---|---|
| Returns |
The code of a clicked key (1..16). If no key is clicked, returns 0. |
| Description |
Call to |
| Requires |
Port needs to be initialized for working with the Keypad library, see Keypad_Init. |
| Example |
var kp : byte; ... kp := Keypad_Key_Click(); |
Library Example
This is a simple example of using the Keypad Library. It supports keypads with 1..4 rows and 1..4 columns. The code being returned by Keypad_Key_Click() function is in range from 1..16. In this example, the code returned is transformed into ASCII codes [0..9,A..F] and displayed on Lcd. In addition, a small single-byte counter displays in the second Lcd row number of key presses.
program Keypad_Test;
var kp, cnt, oldstate : byte;
txt : string[6];
// Keypad module connections
var keypadPort : byte at P0;
// End Keypad module connections
// LCD pinout definition
var LCD_RS : sbit at P2_0_bit;
var LCD_EN : sbit at P2_1_bit;
var LCD_D4 : sbit at P2_2_bit;
var LCD_D5 : sbit at P2_3_bit;
var LCD_D6 : sbit at P2_4_bit;
var LCD_D7 : sbit at P2_5_bit;
// end LCD pinout definitions
begin
oldstate := 0;
cnt := 0; // Reset counter
Keypad_Init(); // Initialize Keypad
Lcd_Init(); // Initialize LCD
Lcd_Cmd(_LCD_CLEAR); // Clear display
Lcd_Cmd(_LCD_CURSOR_OFF); // Cursor off
Lcd_Out(1, 1, 'Key :'); // Write message text on LCD
Lcd_Out(2, 1, 'Times:');
while TRUE do
begin
kp := 0; // Reset key code variable
// Wait for key to be pressed and released
while ( kp = 0 ) do
kp := Keypad_Key_Click(); // Store key code in kp variable
// Prepare value for output, transform key to it's ASCII value
case kp of
//case 10: kp = 42; // '*' // Uncomment this block for keypad4x3
//case 11: kp = 48; // '0'
//case 12: kp = 35; // '#'
//default: kp += 48;
1: kp := 49; // 1 // Uncomment this block for keypad4x4
2: kp := 50; // 2
3: kp := 51; // 3
4: kp := 65; // A
5: kp := 52; // 4
6: kp := 53; // 5
7: kp := 54; // 6
8: kp := 66; // B
9: kp := 55; // 7
10: kp := 56; // 8
11: kp := 57; // 9
12: kp := 67; // C
13: kp := 42; // *
14: kp := 48; // 0
15: kp := 35; // #
16: kp := 68; // D
end;//case
if (kp <> oldstate) then // Pressed key differs from previous
begin
cnt := 1;
oldstate := kp;
end
else // Pressed key is same as previous
Inc(cnt);
Lcd_Chr(1, 10, kp); // Print key ASCII value on LCD
if (cnt = 255) then // If counter varialble overflow
begin
cnt := 0;
Lcd_Out(2, 10, ' ');
end;
WordToStr(cnt, txt); // Transform counter value to string
Lcd_Out(2, 10, txt); // Display counter value on LCD
end;
end.
HW Connection
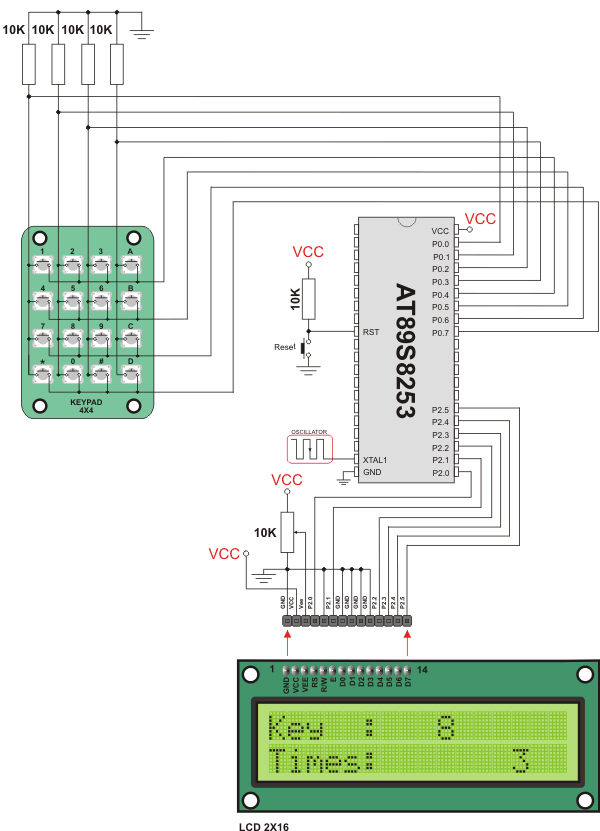
4x4 Keypad connection scheme
What do you think about this topic ? Send us feedback!



