PWM Library
The CCP module is available with a number of dsPIC30/33 and PIC24 MCUs. mikroC PRO for dsPIC30/33 and PIC24 provides a library which simplifies using of the PWM HW Module.
 Important :
PWM module uses either Timer2 or Timer3 module.
Important :
PWM module uses either Timer2 or Timer3 module.
Library Routines
PWM_Init
| Prototype |
unsigned int PWM_Init(unsigned long freq_hz, unsigned int enable_channel_x, unsigned int timer_prescale, unsigned int use_timer_x); // 30F1010 and dsPIC33FJ06GS101/102/202 prototypeunsigned int PWM_Init(unsigned long freq_hz, unsigned int enable_channel_x, unsigned int timer_prescale); |
|---|---|
| Description |
Initializes the PWM module with duty ratio 0. |
| Parameters |
|
| Returns |
|
| Requires |
MCU must have the HW PWM Module. |
| Example |
// Initializes the PWM module at 5KHz, channel 1, no clock prescale, timer2 : unsigned int pwm_period1; ... pwm_period1 = PWM_Init(5000, 1, 0, 2); |
| Notes |
Number of available PWM channels depends on MCU. Refer to MCU datasheet for details. |
PWM_Set_Duty
| Prototype |
void PWM_Set_Duty(unsigned duty, unsigned channel); |
|---|---|
| Description |
The function changes PWM duty ratio. |
| Parameters |
|
| Returns |
Nothing. |
| Requires |
MCU must have the HW PWM Module. PWM channel must be properly initialized. See PWM_Init routine. |
| Example |
// Set channel 1 duty ratio to 50%: unsigned int pwm_period1; ... PWM_Set_Duty(pwm_period1/2, 1); |
| Notes |
Number of available PWM channels depends on MCU. Refer to MCU datasheet for details. |
PWM_Start
| Prototype |
void PWM_Start(char enable_channel_x); |
|---|---|
| Description |
Starts PWM at requested channel. |
| Parameters |
|
| Returns |
Nothing. |
| Requires |
MCU must have the HW PWM Module. PWM channel must be properly configured. See the PWM_Init and PWM_Set_Duty routines. |
| Example |
// start PWM at channel 1 PWM_Start(1); |
| Notes |
Number of available PWM channels depends on MCU. Refer to MCU datasheet for details. |
PWM_Stop
| Prototype |
void PWM_Stop(char disable_channel_x); |
|---|---|
| Description |
Stops PWM at requested channel. |
| Parameters |
|
| Returns |
Nothing. |
| Requires |
MCU must have the HW PWM Module. |
| Example |
// stop PWM at channel 1 PWM_Stop(1); |
| Notes |
Number of available PWM channels depends on MCU. Refer to MCU datasheet for details. |
Library Example
The example changes PWM duty ratio on channels 1 and 2 continuously. If LEDs are connected to channels 1 and 2, a gradual change of emitted light will be noticeable.
unsigned int current_duty, old_duty, current_duty1, old_duty1;
unsigned int pwm_period1, pwm_period2;
void InitMain() {
ADPCFG = 0xFFFF; // Configure AN pins as digital I/O
TRISB = 0xFFFF; // configure PORTB pins as input
PORTD = 0; // set PORTD to 0
TRISD = 0; // designate PORTD pins as output
}
void main() {
InitMain();
current_duty = 16; // initial value for current_duty
current_duty1 = 16; // initial value for current_duty1
pwm_period1 = PWM_Init(5000 , 1, 1, 2);
pwm_period2 = PWM_Init(10000, 2, 1, 3);
PWM_Start(1);
PWM_Start(2);
PWM_Set_Duty(current_duty, 1); // Set current duty for PWM1
PWM_Set_Duty(current_duty1, 2); // Set current duty for PWM2
while (1) { // endless loop
if (RB0_bit) { // button on RB0 pressed
Delay_ms(20);
current_duty++; // increment current_duty
if (current_duty > pwm_period1) { // if we increase current_duty greater then possible pwm_period1 value
current_duty = 0; // reset current_duty value to zero
}
PWM_Set_Duty(current_duty, 1); // set newly acquired duty ratio
}
if (RB1_bit) { // button on RB1 pressed
Delay_ms(20);
current_duty--; // decrement current_duty
if (current_duty > pwm_period1) { // if we decrease current_duty greater then possible pwm_period1 value (overflow)
current_duty = pwm_period1; // set current_duty to max possible value
}
PWM_Set_Duty(current_duty, 1); // set newly acquired duty ratio
}
if (RB2_bit) { // button on RB2 pressed
Delay_ms(20);
current_duty1++; // increment current_duty1
if (current_duty1 > pwm_period2) { // if we increase current_duty1 greater then possible pwm_period2 value
current_duty1 = 0; // reset current_duty1 value to zero
}
PWM_Set_Duty(current_duty1, 2); // set newly acquired duty ratio
}
if (RB3_bit) { // button on RB3 pressed
Delay_ms(20);
current_duty1--; // decrement current_duty1
if (current_duty1 > pwm_period2) { // if we decrease current_duty1 greater then possible pwm_period1 value (overflow)
current_duty1 = pwm_period2; // set current_duty to max possible value
}
PWM_Set_Duty(current_duty1, 2);
}
Delay_ms(5); // slow down change pace a little
}
}
HW Connection
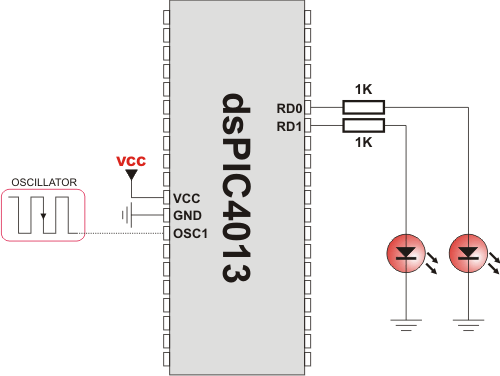
PWM demonstration
What do you think about this topic ? Send us feedback!




