SPI Library
mikroC PRO for 8051 provides a library for comfortable with SPI work in Master mode. The 8051 MCU can easily communicate with other devices via SPI: A/D converters, D/A converters, MAX7219, LTC1290, etc.
Library Routines
Generic Routines
Notes:
- SPI routines require you to specify the module you want to use. To select the desired SPI, simply change the letter
xin the prototype for a number from1to2.
Number of SPI modules per MCU differs from chip to chip. Please, read the appropriate datasheet before utilizing this library. - Some MCUs have multiple SPI modules. Switching between the SPI modules in the SPI library is done by the SPI_Set_Active function (SPI module has to be previously initialized).
- Some of the MCUs do not support SPIx_Init_Advanced routine. Please, refer to the appropriate datasheet.
SPIx_Init
| Prototype |
// for ATMEL MCUs
// for Silicon Laboratories MCUs |
|---|---|
| Returns |
Nothing. |
| Description |
This routine configures and enables SPI module with the following settings:
|
| Requires |
MCU must have SPI module. |
| Example |
// Initialize the SPI module with default settings SPI1_Init(); // Initialize the SPI module with the baud rate of 100000 SPI1_Init(100000); |
SPIx_Init_Advanced
| Prototype |
// for ATMEL MCUs
// for Silicon Laboratories MCUs |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Returns |
Nothing. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description |
This routine configures and enables the SPI module with the user defined settings. Parameters :
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Requires |
MCU must have SPI module. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Example |
// SPI configuration for ATMEL MCU's: clock = Fosc/4 , clock IDLE state low, data transmitted at low to high clock edge and output mode 8051: SPI1_Init_Advanced(_SPI_FCY_DIV4 | _SPI_CLK_IDLE_LO | _SPI_CLK_IDLE_2_ACTIVE | _SPI_OUTPUT_8051) // SPI configuration for Silicon Laboratories MCU's: clock = 100000, clock IDLE state low and data transmitted at low to high clock edge: SPI1_Init_Advanced(100000, _SPI_CLK_IDLE_LO | _SPI_CLK_IDLE_2_ACTIVE) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SPIx_Read
| Prototype |
unsigned short SPIx_Read(unsigned short buffer); |
|---|---|
| Returns |
Received data. |
| Description |
Reads one byte from the SPI bus. Parameters :
|
| Requires |
SPI module must be initialized before using this function. See SPIx_Init and SPIx_Init_Advanced routines. |
| Example |
// read a byte from the SPI bus unsigned short take, dummy1; ... take = SPI1_Read(dummy1); |
SPIx_Write
| Prototype |
void SPIx_Write(unsigned short wrdata); |
|---|---|
| Returns |
Nothing. |
| Description |
Writes byte via the SPI bus. Parameters :
|
| Requires |
SPI module must be initialized before using this function. See SPIx_Init and SPIx_Init_Advanced routines. |
| Example |
// write a byte to the SPI bus char buffer; ... SPI1_Write(buffer); |
SPI_Set_Active
| Prototype |
void SPI_Set_Active(char (*read_ptr)(char), void(*write_ptr)(char)); |
|---|---|
| Returns |
Nothing. |
| Description |
Sets the active SPI module which will be used by the SPI routines. Parameters :
|
| Requires |
Routine is available only for MCUs with two SPI modules. Used SPI module must be initialized before using this function. See SPIx_Init and SPIx_Init_Advanced routines.
|
| Example |
SPI_Set_Active(&SPI2_Read); // Sets the SPI2 module active |
SPI_Read
| Prototype |
unsigned short SPI_Read(unsigned short buffer); |
|---|---|
| Returns |
Received data. |
| Description |
Reads one byte from the SPI bus. This is a generic routine which uses the active SPI module previously activated by the SPI_Set_Active routine. Parameters :
|
| Requires |
You need MCU with hardware integrated SPI. SPI must be initialized and communication established before using this function. See SPIx_Init_Advanced or SPIx_Init. |
| Example |
short take, buffer; ... take = SPI_Read(buffer); |
SPI_Write
| Prototype |
void SPI_Write(unsigned short data_); |
|---|---|
| Returns |
Nothing. |
| Description |
Writes byte via the SPI bus. This is a generic routine which uses the active SPI module previously activated by the SPI_Set_Active routine. Parameters :
|
| Requires |
You need MCU with hardware integrated SPI. SPI must be initialized and communication established before using this function. See SPIx_Init_Advanced or SPIx_Init. |
| Example |
// write a byte to the SPI bus char buffer; ... SPI_Write(buffer); |
Library Example
The code demonstrates how to use SPI library functions for communication between SPI module of the MCU and Microchip's MCP4921 12-bit D/A converter
// DAC module connections
sbit DAC_CS at P3_4_bit;
// End DAC module connections
unsigned int value;
// DAC increments (0..4095) --> output voltage (0..Vref)
void DAC_Output(unsigned int valueDAC) {
char temp;
DAC_CS = 0; // select MCP4921
// Send High Byte
temp = (valueDAC >> 8) & 0x0F; // Store valueDAC[11..8] to temp[3..0]
temp |= 0x30; // Define DAC setting http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/21897B.pdf#page=18&zoom=100
SPI1_Write(temp); // Send high byte via SPI
// Send Low Byte
temp = valueDAC; // Store valueDAC[7..0] to temp[7..0]
SPI1_Write(temp); // Send low byte via SPI
DAC_CS = 1; // deselect MCP4921
}
void main() {
DAC_CS = 1; // deselect MCP4921
SPI1_Init(); // Initialize SPI module
value = 2048; // When program starts, DAC gives
// the output in the mid-range
while (1) { // Endless loop
if ((!P0_0_bit) && (value < 4095)) { // If P0.0 button is pressed
value++; // increment value
}
else {
if ((!P0_1_bit) && (value > 0)) { // If P0.1 button is pressed
value--; // decrement value
}
}
DAC_Output(value); // Send value to DAC chip
Delay_ms(1); // Slow down key repeat pace
}
}
HW Connection
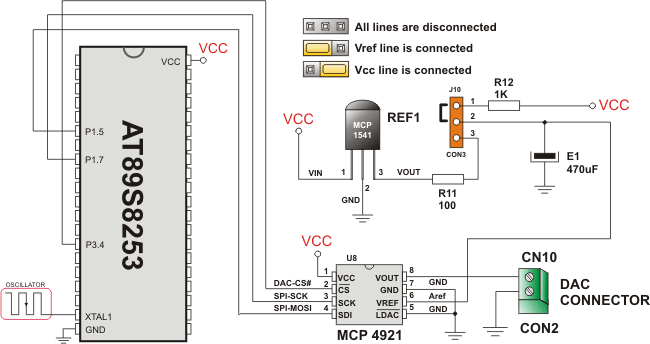
SPI HW connection
What do you think about this topic ? Send us feedback!



