PS/2 Library
The mikroPascal PRO for PIC32 provides a library for communication with the common PS/2 keyboard.
 Important :
Important :
- The library does not utilize interrupts for data retrieval, and requires the oscillator clock to be at least 6MHz.
- The pins to which a PS/2 keyboard is attached should be connected to the pull-up resistors.
- Although PS/2 is a two-way communication bus, this library does not provide MCU-to-keyboard communication; e.g. pressing the Caps Lock key will not turn on the Caps Lock LED.
External dependencies of PS/2 Library
| The following variables must be defined in all projects using PS/2 Library: | Description : | Example : |
|---|---|---|
var PS2_Data : sbit; sfr; atomic; external; |
PS/2 Data line. | var PS2_Data : sbit at RB0_bit; |
var PS2_Clock : sbit; sfr; atomic; external; |
PS/2 Clock line. | var PS2_Clock : sbit at RB1_bit; |
var PS2_Data_Direction : sbit; sfr; atomic; external; |
Direction of the PS/2 Data pin. | var PS2_Data_Direction : sbit at TRISB0_bit; |
var PS2_Clock_Direction : sbit; sfr; atomic; external; |
Direction of the PS/2 Clock pin. | var PS2_Clock_Direction : sbit at TRISB1_bit; |
Library Routines
Ps2_Config
| Prototype |
procedure Ps2_Config(); |
|---|---|
| Description |
Initializes the MCU for work with the PS/2 keyboard. |
| Parameters |
None. |
| Returns |
Nothing. |
| Requires |
Global variables :
|
| Example |
// PS2 pinout definition var PS2_Data : sbit at RB0_bit; var PS2_Clock : sbit at RB1_bit; var PS2_Data_Direction : sbit at TRISB0_bit; var PS2_Clock_Direction : sbit at TRISB1_bit; // End of PS2 pinout definition// Init PS/2 Keyboard |
| Notes |
None. |
Ps2_Key_Read
| Prototype |
function Ps2_Key_Read(var value : byte; var special : byte; var pressed : byte) : word; |
|---|---|
| Description |
The function retrieves information on key pressed. |
| Parameters |
|
| Returns |
|
| Requires |
PS/2 keyboard needs to be initialized. See Ps2_Config routine. |
| Example |
var value, special, pressed : word;
...
// Press Enter to continue:
repeat {
if (Ps2_Key_Read(value, special, pressed)) then
if ((value = 13) and (special = 1)) then break;
until (0=1);
|
| Notes |
None. |
Special Function Keys
| Key | Value returned |
|---|---|
| F1 | 1 |
| F2 | 2 |
| F3 | 3 |
| F4 | 4 |
| F5 | 5 |
| F6 | 6 |
| F7 | 7 |
| F8 | 8 |
| F9 | 9 |
| F10 | 10 |
| F11 | 11 |
| F12 | 12 |
| Enter | 13 |
| Page Up | 14 |
| Page Down | 15 |
| Backspace | 16 |
| Insert | 17 |
| Delete | 18 |
| Windows | 19 |
| Ctrl | 20 |
| Shift | 21 |
| Alt | 22 |
| Print Screen | 23 |
| Pause | 24 |
| Caps Lock | 25 |
| End | 26 |
| Home | 27 |
| Scroll Lock | 28 |
| Num Lock | 29 |
| Left Arrow | 30 |
| Right Arrow | 31 |
| Up Arrow | 32 |
| Down Arrow | 33 |
| Escape | 34 |
| Tab | 35 |
Library Example
This simple example reads values of the pressed keys on the PS/2 keyboard and sends them via UART.
program PS2_Example;
var keydata, special, down : byte;
var PS2_Data : sbit at RD0_bit;
PS2_Clock : sbit at RD1_bit;
PS2_Data_Direction : sbit at TRISD0_bit;
PS2_Clock_Direction : sbit at TRISD1_bit;
begin
CHECON := 0x32;
AD1PCFG := 0xFFFF; // Configure AN pins as digital I/O
UART1_Init(56000); // Initialize UART module at 19200 bps
Ps2_Config(); // Init PS/2 Keyboard
Delay_ms(100); // Wait for keyboard to finish
UART1_Write_Text('Ready'); // Ready
UART1_Write(13); // Line Feed
UART1_Write(10); // Carriage return
while TRUE do // Endless loop
begin
if Ps2_Key_Read(keydata, special, down) then // If data was read from PS/2
begin
if (down <> 0) and (keydata = 16) then // Backspace
begin
UART1_Write(0x08); // Send Backspace to usart terminal
end
else if (down <> 0) and (keydata = 13) then // Enter
begin
UART1_Write(10); // Send carriage return to usart terminal
UART1_Write(13); // Uncomment this line if usart terminal also expects line feed
// for new line transition
end
else if (down <> 0) and (special = 0) and (keydata <> 0) then // Common key read
begin
UART1_Write(keydata); // Send key to usart terminal
end;
end;
Delay_ms(1); // Debounce period
end;
end.
HW Connection
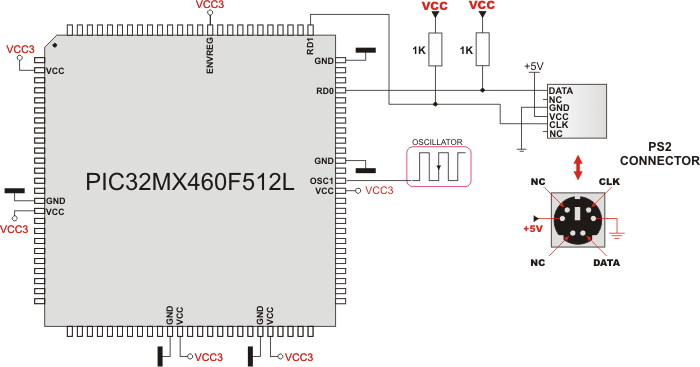
Example of PS2 keyboard connection
Copyright (c) 2002-2012 mikroElektronika. All rights reserved.
What do you think about this topic ? Send us feedback!
What do you think about this topic ? Send us feedback!




