RS-485 Library
RS-485 is a multipoint communication which allows multiple devices to be connected to a single bus. The mikroPascal PRO for 8051 provides a set of library routines for comfortable work with RS485 system using Master/Slave architecture. Master and Slave devices interchange packets of information. Each of these packets contains synchronization bytes, CRC byte, address byte and the data. Each Slave has unique address and receives only packets addressed to it. The Slave can never initiate communication.
It is the user’s responsibility to ensure that only one device transmits via 485 bus at a time.
The RS-485 routines require the UART module. Pins of UART need to be attached to RS-485 interface transceiver, such as LTC485 or similar (see schematic at the bottom of this page).
Note: The library uses the UART module for communication. The user must initialize the appropriate UART module before using the
RS-485 Library. For MCUs with two UART modules it is possible to initialize both of them and then switch by
using the UART_Set_Active function. See the UART Library functions.
- START byte value =
150 - STOP byte value =
169 - Address
50is the broadcast address for all Slaves (packets containing address50will be received by all Slaves except the Slaves with addresses150and169).
External dependencies of RS-485 Library
| The following variable must be defined in all projects using RS-485 Library: | Description : | Example : |
|---|---|---|
var rs485_transceive: sbit; bdata; sfr; external; |
Control RS-485 Transmit/Receive operation mode | var rs485_transceive: sbit at P3_2_bit; |
Library Routines
- RS485Master_Init
- RS485Master_Receive
- RS485Master_Send
- RS485Slave_Init
- RS485Slave_Receive
- RS485Slave_Send
RS485Master_Init
| Prototype |
procedure RS485Master_Init(); |
|---|---|
| Returns |
Nothing. |
| Description |
Initializes MCU as a Master for RS-485 communication. |
| Requires |
UART HW module needs to be initialized. See UARTx_Init. |
| Example |
// rs485 module pinout var rs485_transceive : sbit at P3_2_bit; // transmit/receive control set to P3.B2 ... UART1_Init(9600); // initialize UART1 module RS485Master_Init(); // intialize MCU as a Master for RS-485 communication |
RS485Master_Receive
| Prototype |
procedure RS485Master_Receive(var data_buffer: array[5] of byte); |
|---|---|
| Returns |
Nothing. |
| Description |
Receives messages from Slaves. Messages are multi-byte, so this routine must be called for each byte received. Parameters :
The function automatically adjusts |
| Requires |
MCU must be initialized as a Master for RS-485 communication. See RS485Master_Init. |
| Example |
var msg : array[20] of byte; ... RS485Master_Receive(msg); |
RS485Master_Send
| Prototype |
procedure RS485Master_Send(var data_buffer: array[20] of byte; datalen: byte; slave_address: byte); |
|---|---|
| Returns |
Nothing. |
| Description |
Sends message to Slave(s). Message format can be found at the bottom of this page. Parameters :
|
| Requires |
MCU must be initialized as a Master for RS-485 communication. See RS485Master_Init. It is the user’s responsibility to ensure (by protocol) that only one device sends data via 485 bus at a time. |
| Example |
var msg : array[20] of byte; ... // send 3 bytes of data to Slave with address 0x12 RS485Master_Send(msg, 3, 0x12); |
RS485Slave_Init
| Prototype |
procedure RS485Slave_Init(slave_address: byte); |
|---|---|
| Returns |
Nothing. |
| Description |
Initializes MCU as a Slave for RS-485 communication. Parameters :
|
| Requires |
UART HW module needs to be initialized. See UARTx_Init. |
| Example |
// rs485 module pinout var rs485_transceive : sbit at P3_2_bit; // transmit/receive control set to P3.B2 ... UART1_Init(9600); // initialize UART1 module RS485Slave_Init(160); // intialize MCU as a Slave for RS-485 communication with address 160 |
RS485Slave_Receive
| Prototype |
procedure RS485Slave_Receive(var data_buffer: array[20] of byte); |
|---|---|
| Returns |
Nothing. |
| Description |
Receives messages from Master. If Slave address and Message address field don't match then the message will be discarded. Messages are multi-byte, so this routine must be called for each byte received. Parameters :
The function automatically adjusts |
| Requires |
MCU must be initialized as a Slave for RS-485 communication. See RS485Slave_Init. |
| Example |
var msg : array[20] of byte; ... RS485Slave_Read(msg); |
RS485Slave_Send
| Prototype |
procedure RS485Slave_Send(var data_buffer: array[20] of byte; datalen : byte); |
|---|---|
| Returns |
Nothing. |
| Description |
Sends message to Master. Message format can be found at the bottom of this page. Parameters :
|
| Requires |
MCU must be initialized as a Slave for RS-485 communication. See RS485Slave_Init. It is the user’s responsibility to ensure (by protocol) that only one device sends data via 485 bus at a time. |
| Example |
var msg : array[8] of byte; ... // send 2 bytes of data to the Master RS485Slave_Send(msg, 2); |
Library Example
This is a simple demonstration of RS485 Library routines usage.
Master sends message to Slave with address 160 and waits for a response. The Slave accepts data, increments it and sends it back to the Master. Master then does the same and sends incremented data back to Slave, etc.
Master displays received data on P0, while error on receive (0xAA) and number of consecutive unsuccessful retries are displayed on P1. Slave displays received data on P0, while error on receive (0xAA) is displayed on P1. Hardware configurations in this example are made for the Easy8051B board and AT89S8253.
RS485 Master code:
program RS485_Master;
var dat : array[20] of byte ; // Buffer for receving/sending messages
counter, j : byte;
cnt : longint;
// RS485 module connections
var rs485_transceive : sbit at P3_2_bit; // Transmit/Receive control set to P3.2
// End RS485 module connections
// Interrupt routine
procedure interrupt(); org IVT_ADDR_ES;
begin
EA_bit := 0; // Clear global interrupt enable flag
if ( RI_bit ) then // Test UART receive interrupt flag
begin
Rs485master_Receive(dat); // UART receive interrupt detected,
// receive data using RS485 communication
RI_bit := 0; // Clear UART interrupt flag
end;
EA_bit := 1; // Set global interrupt enable flag
end;
begin
cnt := 0;
P0 := 0; // Clear ports
P1 := 0;
UART1_Init(4800); // Initialize UART module at 9600 bps
Delay_ms(100);
Rs485master_Init(); // Intialize MCU as RS485 master
dat[0] := 0xAA; // Fill buffer
dat[1] := 0xF0;
dat[2] := 0x0F;
dat[4] := 0; // Ensure that message received flag is 0
dat[5] := 0; // Ensure that error flag is 0
dat[6] := 0;
Rs485master_Send( dat, 1, 160 );
ES_bit := 1; // Enable UART interrupt
RI_bit := 0; // Clear UART RX interrupt flag
EA_bit := 1; // Enable interrupts
while TRUE do // Endless loop
begin // Upon completed valid message receiving
// data[4] is set to 255
Inc(cnt); // Increment loop pass counter
if (dat[5] <> 0) then // If error detected, signal it by
P1 := 0xAA; // setting PORT1 to 0xAA
if (dat[4] <> 0) then // If message received successfully
begin
cnt := 0; // Reset loop pass counter
dat[4] := 0; // Clear message received flag
j := dat[3]; // Read number of message received bytes
for counter := 1 to j do
P0 := dat[counter-1]; // Show received data on PORT0
Inc(dat[0]); // Increment first received byte dat[0]
Delay_ms(1);
Rs485master_Send(dat,1,160); // And send it back to Slave
end;
if ( cnt > 10000 ) then // If loop is passed 100000 times with
begin // no message received
Inc(P2); // Signal receive message failure on PORT2
cnt := 0; // Reset loop pass counter
Rs485master_Send(dat,1,160); // Retry send message
if (P2 > 10) then // If sending failed 10 times
Rs485master_Send(dat,1,50); // Send message on broadcast address
end;
end;
end.
RS485 Slave code:
program RS485_Slave;
var dat : array[20] of byte; // Buffer for receving/sending messages
counter, j : byte;
// RS485 module connections
var rs485_transceive : sbit at P3_2_bit; // Transmit/Receive control set to P3.2
// End RS485 module connections
//-------------- Interrupt routine
procedure interrupt(); org IVT_ADDR_ES;
begin
EA_bit := 0; // Clear global interrupt enable flag
if ( RI_bit ) then // Test UART receive interrupt flag
begin
Rs485slave_Receive(dat); // UART receive interrupt detected,
// receive data using RS485 communication
RI_bit := 0; // Clear UART interrupt flag
end;
EA_bit := 1; // Set global interrupt enable flag
end;
begin
P0 := 0; // Clear ports
P1 := 0;
UART1_Init(4800); // Initialize UART module at 9600 bps
Delay_ms(100);
Rs485slave_Init(160); // Intialize MCU as slave, address 160
dat[4] := 0; // ensure that message received flag is 0
dat[5] := 0; // ensure that error flag is 0
dat[6] := 0; // ensure that error flag is 0
ES_bit := 1; // Enable UART interrupt
RI_bit := 0; // Clear UART RX interrupt flag
EA_bit := 1; // Enable interrupts
while TRUE do // Endless loop
begin
// Upon completed valid message receiving
// data[4] is set to 255
if ( dat[5] <> 0) then // If error detected, signal it by
begin
P1 := 0xAA; // setting PORT1 to 0xAA
dat[5] := 0;
end;
if (dat[4] <> 0) then // If message received successfully
begin
dat[4] := 0; // Clear message received flag
j := dat[3]; // Read number of message received bytes
for counter := 1 to j do
P0 := dat[counter-1]; // Show received data on PORT0
Inc(dat[0]); // Increment received dat[0]
Delay_ms(1);
Rs485slave_Send(dat,1); // And send back to Master
end;
end;
end.
HW Connection
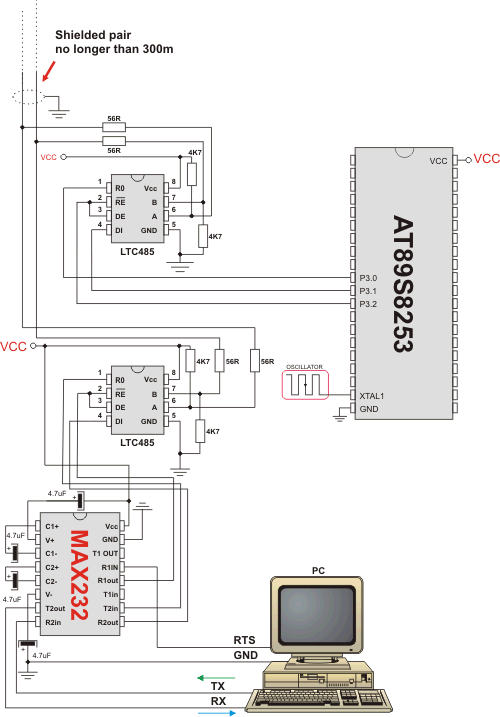
Example of interfacing PC to 8051 MCU via RS485 bus with LTC485 as RS-485 transceiver
Message format and CRC calculations
Q: How is CRC checksum calculated on RS485 Master side?
_RS485_START_BYTE := 0x96; // 10010110
_RS485_STOP_BYTE := 0xA9; // 10101001
PACKAGE:
--------
_RS485_START_BYTE 0x96
ADDRESS
DATALEN
[DATA1] // if exists
[DATA2] // if exists
[DATA3] // if exists
CRC
_RS485_STOP_BYTE 0xA9
DATALEN bits
------------
bit7 := 1 MASTER SENDS
0 SLAVE SENDS
bit6 := 1 ADDRESS WAS XORed with 1, IT WAS EQUAL TO _RS485_START_BYTE or _RS485_STOP_BYTE
0 ADDRESS UNCHANGED
bit5 := 0 FIXED
bit4 := 1 DATA3 (if exists) WAS XORed with 1, IT WAS EQUAL TO _RS485_START_BYTE or _RS485_STOP_BYTE
0 DATA3 (if exists) UNCHANGED
bit3 := 1 DATA2 (if exists) WAS XORed with 1, IT WAS EQUAL TO _RS485_START_BYTE or _RS485_STOP_BYTE
0 DATA2 (if exists) UNCHANGED
bit2 := 1 DATA1 (if exists) WAS XORed with 1, IT WAS EQUAL TO _RS485_START_BYTE or _RS485_STOP_BYTE
0 DATA1 (if exists) UNCHANGED
bit1bit0 := 0 to 3 NUMBER OF DATA BYTES SEND
CRC generation :
----------------
crc_send := datalen xor address;
crc_send := crc_send xor data[0]; // if exists
crc_send := crc_send xor data[1]; // if exists
crc_send := crc_send xor data[2]; // if exists
crc_send := not crc_send;
if ((crc_send = _RS485_START_BYTE) or (crc_send = _RS485_STOP_BYTE)) then
Inc(crc_send);
NOTE: DATALEN<4..0> can not take the _RS485_START_BYTE<4..0> or _RS485_STOP_BYTE<4..0> values.
What do you think about this topic ? Send us feedback!



