Manchester Code Library
The mikroC PRO for ARM provides a library for handling Manchester coded signals. The Manchester code is a code in which data and clock signals are combined to form a single self-synchronizing data stream; each encoded bit contains a transition at the midpoint of a bit period, the direction of transition determines whether the bit is 0 or 1; the second half is the true bit value and the first half is the complement of the true bit value (as shown in the figure below).
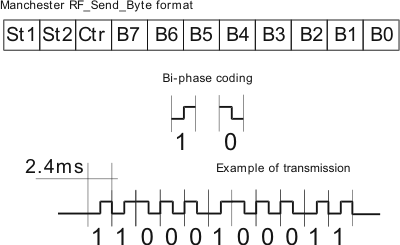
 Important :
Important :
- The Manchester receive routines are blocking calls (
Man_Receive_InitandMan_Synchro). This means that MCU will wait until the task has been performed (e.g. byte is received, synchronization achieved, etc). - Manchester code library implements time-based activities, so interrupts need to be disabled when using it.
External dependencies of Manchester Code Library
Stellaris
| The following variables must be defined in all projects using Manchester Code Library: | Description: | Example: |
|---|---|---|
extern sfr sbit MANRXPIN; |
Receive line. | sbit MANRXPIN at GPIO_PORTE_DATA.B0; |
extern sfr sbit MANTXPIN; |
Transmit line. | sbit MANTXPIN at GPIO_PORTE_DATA.B1; |
extern sfr sbit GPIO_PORTE_DIR.B0; |
Direction of the Receive pin. | sbit MANRXPIN_Direction at GPIO_PORTE_DIR.B0; |
extern sfr sbit MANTXPIN_Direction; |
Direction of the Transmit pin. | sbit MANTXPIN_Direction at GPIO_PORTE_DIR.B1; |
STM32
| The following variables must be defined in all projects using Manchester Code Library: | Description: | Example: |
|---|---|---|
extern sfr sbit MANRXPIN; |
Receive line. | sbit MANRXPIN at GPIOE_IDR.B8; |
extern sfr sbit MANTXPIN; |
Transmit line. | sbit MANTXPIN at GPIOE_ODR.B9; |
Library Routines
The following routines are for the internal use by compiler only:
- Manchester_0
- Manchester_1
- Manchester_Out
Man_Receive_Init
| Prototype |
unsigned int Man_Receive_Init(); |
|---|---|
| Description |
The function configures Receiver pin. After that, the function performs synchronization procedure in order to retrieve baud rate out of the incoming signal. |
| Parameters |
None. |
| Returns |
|
| Requires |
External dependencies of the library from the top of the page must be defined before using this function. |
| Example |
Stellaris
// Manchester module connections
sbit MANRXPIN at GPIO_PORTE_DATA.B0;
sbit MANRXPIN_Direction at GPIO_PORTE_DIR.B0;
sbit MANTXPIN at GPIO_PORTE_DATA.B1;
sbit MANTXPIN_Direction at GPIO_PORTE_DIR.B1;
...
if (Man_Receive_Init() == 0) {
...
}
STM32
// Manchester module connections
sbit MANRXPIN at GPIOE_IDR.B8;
sbit MANTXPIN at GPIOE_IDR.B9;
...
if (Man_Receive_Init() == 0) {
...
}
|
| Notes |
In case of multiple persistent errors on reception, the user should call this routine once again or Man_Synchro routine to enable synchronization. |
Man_Receive
| Prototype |
unsigned char Man_Receive(unsigned int *error); |
|---|---|
| Description |
The function extracts one byte from incoming signal. |
| Parameters |
|
| Returns |
A byte read from the incoming signal. |
| Requires |
To use this function, the user must prepare the MCU for receiving. See Man_Receive_Init routines. |
| Example |
unsigned int data = 0, error = 0;
...
data = Man_Receive(&error);
if (error)
{ /* error handling */ }
|
| Notes |
None. |
Man_Send_Init
| Prototype |
void Man_Send_Init(); |
|---|---|
| Description |
The function configures Transmitter pin. |
| Parameters |
None. |
| Returns |
Nothing. |
| Requires |
External dependencies of the library from the top of the page must be defined before using this function. |
| Example |
Stellaris
// Manchester module connections
sbit MANRXPIN at GPIO_PORTE_DATA.B0;
sbit MANRXPIN_Direction at GPIO_PORTE_DIR.B0;
sbit MANTXPIN at GPIO_PORTE_DATA.B1;
sbit MANTXPIN_Direction at GPIO_PORTE_DIR.B1;
...
if (Man_Receive_Init() == 0) {
...
}
STM32
// Manchester module connections
sbit MANRXPIN at GPIOE_IDR.B8;
sbit MANTXPIN at GPIOE_IDR.B9;
...
if (Man_Receive_Init() == 0) {
...
}
|
| Notes |
None. |
Man_Send
| Prototype |
void Man_Send(unsigned char tr_data); |
|---|---|
| Description |
Sends one byte. |
| Parameters |
|
| Returns |
Nothing. |
| Requires |
To use this function, the user must prepare the MCU for sending. See Man_Send_Init routine. |
| Example |
unsigned int msg; ... Man_Send(msg); |
| Notes |
Baud rate used is 500 bps. |
Man_Synchro
| Prototype |
unsigned int Man_Synchro(); |
|---|---|
| Description |
Measures half of the manchester bit length with 10us resolution. |
| Parameters |
None. |
| Returns |
|
| Requires |
To use this function, you must first prepare the MCU for receiving. See Man_Receive_Init. |
| Example |
unsigned int man__half_bit_len; ... man__half_bit_len = Man_Synchro(); |
| Notes |
None. |
Man_Break
| Prototype |
void Man_Break(); |
|---|---|
| Description |
Man_Receive is blocking routine and it can block the program flow. Call this routine from interrupt to unblock the program execution. This mechanism is similar to WDT. |
| Parameters |
None. |
| Returns |
Nothing. |
| Requires |
Nothing. |
| Example |
|
| Notes |
Interrupts should be disabled before using Manchester routines again (see note at the top of this page). |
Library Example
The following code is code for the Manchester receiver, it shows how to use the Manchester Library for receiving data:
Stellaris
// LCD module connections
sbit LCD_RS at GPIO_PORTD_DATA2_bit;
sbit LCD_EN at GPIO_PORTD_DATA3_bit;
sbit LCD_D4 at GPIO_PORTD_DATA4_bit;
sbit LCD_D5 at GPIO_PORTD_DATA5_bit;
sbit LCD_D6 at GPIO_PORTD_DATA6_bit;
sbit LCD_D7 at GPIO_PORTD_DATA7_bit;
sbit LCD_RS_Direction at GPIO_PORTD_DIR2_bit;
sbit LCD_EN_Direction at GPIO_PORTD_DIR3_bit;
sbit LCD_D4_Direction at GPIO_PORTD_DIR4_bit;
sbit LCD_D5_Direction at GPIO_PORTD_DIR5_bit;
sbit LCD_D6_Direction at GPIO_PORTD_DIR6_bit;
sbit LCD_D7_Direction at GPIO_PORTD_DIR7_bit;
// End LCD module connections
// Manchester module connections
sbit MANRXPIN at GPIO_PORTE_DATA.B0;
sbit MANRXPIN_Direction at GPIO_PORTE_DIR.B0;
sbit MANTXPIN at GPIO_PORTE_DATA.B1;
sbit MANTXPIN_Direction at GPIO_PORTE_DIR.B1;
// End Manchester module connections
unsigned int error;
char ErrorCount, chr_counter, byte_rcvd;
void main() {
ErrorCount = 0;
chr_counter = 0;
Lcd_Init(); // Initialize LCD
Lcd_Cmd(_LCD_CLEAR); // Clear LCD display
Man_Receive_Init(); // Initialize Receiver
while (1) { // Endless loop
Lcd_Cmd(_LCD_FIRST_ROW); // Move cursor to the 1st row
while (1) { // Wait for the "start" byte
byte_rcvd = Man_Receive(&error); // Attempt byte receive
if (byte_rcvd == 0x0B) // "Start" byte, see Transmitter example
break; // We got the starting sequence
if (error) // Exit so we do not loop forever
break;
}
do
{
byte_rcvd = Man_Receive(&error); // Attempt byte receive
if (error) { // If error occured
Lcd_Chr_CP('?'); // Write question mark on LCD
ErrorCount++; // Update error counter
if (ErrorCount > 20) { // In case of multiple errors
Man_Synchro(); // Try to synchronize again
//Man_Receive_Init(); // Alternative, try to Initialize Receiver again
ErrorCount = 0; // Reset error counter
}
}
else { // No error occured
if (byte_rcvd != 0x0E) { // If "End" byte was received(see Transmitter example)
// do not write anymore received byte on LCD
Lcd_Chr_CP(byte_rcvd); // else write character on LCD
chr_counter++; // Counts how many chars have been written on LCD
if (chr_counter == 25) { // If there were more then 25 characters
// synchronization is off
Lcd_Cmd(_LCD_CLEAR); // Clear the LCD of garbled communication
Man_Synchro(); // Try to synchronize again
}
}
else
chr_counter = 0; // reset chr_counter
}
Delay_ms(25);
}
while (byte_rcvd != 0x0E); // If "End" byte was received exit do loop
}
}
STM32
// LCD module connections
sbit LCD_RS at GPIOD_ODR.B2;
sbit LCD_EN at GPIOD_ODR.B3;
sbit LCD_D4 at GPIOD_ODR.B4;
sbit LCD_D5 at GPIOD_ODR.B5;
sbit LCD_D6 at GPIOD_ODR.B6;
sbit LCD_D7 at GPIOD_ODR.B7;
// End LCD module connections
// Manchester module connections
sbit MANRXPIN at GPIOE_IDR.B8;
sbit MANTXPIN at GPIOE_ODR.B9;
// End Manchester module connections
unsigned int error;
char ErrorCount, chr_counter, byte_rcvd;
void main() {
ErrorCount = 0;
chr_counter = 0;
Lcd_Init(); // Initialize LCD
Lcd_Cmd(_LCD_CLEAR); // Clear LCD display
Man_Receive_Init(); // Initialize Receiver
while (1) { // Endless loop
Lcd_Cmd(_LCD_FIRST_ROW); // Move cursor to the 1st row
while (1) { // Wait for the "start" byte
byte_rcvd = Man_Receive(&error); // Attempt byte receive
if (byte_rcvd == 0x0B) // "Start" byte, see Transmitter example
break; // We got the starting sequence
if (error) // Exit so we do not loop forever
break;
}
do
{
byte_rcvd = Man_Receive(&error); // Attempt byte receive
if (error) { // If error occured
Lcd_Chr_CP('?'); // Write question mark on LCD
ErrorCount++; // Update error counter
if (ErrorCount > 20) { // In case of multiple errors
Man_Synchro(); // Try to synchronize again
//Man_Receive_Init(); // Alternative, try to Initialize Receiver again
ErrorCount = 0; // Reset error counter
}
}
else { // No error occured
if (byte_rcvd != 0x0E) { // If "End" byte was received(see Transmitter example)
// do not write anymore received byte on LCD
Lcd_Chr_CP(byte_rcvd); // else write character on LCD
chr_counter++; // Counts how many chars have been written on LCD
if (chr_counter == 25) { // If there were more then 25 characters
// synchronization is off
Lcd_Cmd(_LCD_CLEAR); // Clear the LCD of garbled communication
Man_Synchro(); // Try to synchronize again
}
}
else
chr_counter = 0; // reset chr_counter
}
Delay_ms(25);
}
while (byte_rcvd != 0x0E); // If "End" byte was received exit do loop
}
}
The following code is code for the Manchester transmitter, it shows how to use the Manchester Library for transmitting data:
Stellaris
// Manchester module connections
sbit MANRXPIN at GPIO_PORTE_DATA.B0;
sbit MANRXPIN_Direction at GPIO_PORTE_DIR.B0;
sbit MANTXPIN at GPIO_PORTE_DATA.B1;
sbit MANTXPIN_Direction at GPIO_PORTE_DIR.B1;
// End Manchester module connections
char index, character;
char s1[] = "mikroElektronika";
void main() {
Man_Send_Init(); // Initialize transmitter
while (1) { // Endless loop
Man_Send(0x0B); // Send "start" byte
Delay_ms(100); // Wait for a while
character = s1[0]; // Take first char from string
index = 0; // Initialize index variable
while (character) { // String ends with zero
Man_Send(character); // Send character
Delay_ms(90); // Wait for a while
index++; // Increment index variable
character = s1[index]; // Take next char from string
}
Man_Send(0x0E); // Send "end" byte
Delay_ms(1000);
}
}
STM32
// Manchester module connections
sbit MANRXPIN at GPIOE_IDR.B8;
sbit MANTXPIN at GPIOE_ODR.B9;
// End Manchester module connections
char index, character;
char s1[] = "mikroElektronika";
void main() {
Man_Send_Init(); // Initialize transmitter
while (1) { // Endless loop
Man_Send(0x0B); // Send "start" byte
Delay_ms(100); // Wait for a while
character = s1[0]; // Take first char from string
index = 0; // Initialize index variable
while (character) { // String ends with zero
Man_Send(character); // Send character
Delay_ms(90); // Wait for a while
index++; // Increment index variable
character = s1[index]; // Take next char from string
}
Man_Send(0x0E); // Send "end" byte
Delay_ms(1000);
}
}
What do you think about this topic ? Send us feedback!




